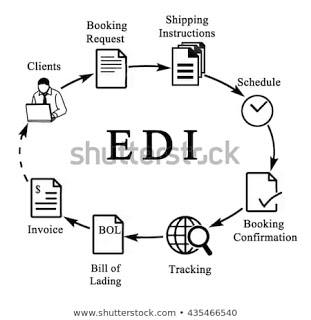
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) is the transfer of data from one computer system to another by standardized message formatting, without the need for human intervention. It permits multiple companies from different countries to exchange documents electronically. It’s done through serial links and peer-to-peer networks, though most exchanges currently rely on the Internet for connectivity.
An EDI message contains a string of data elements, each of which would hold the information on purchase order, product model and many separated by delimiter. The entire string is called as data segment. One or more data segments wrapper within a header and a trailer segment forms the complete EDI data unit.
Both parties and the trading partners should be in the same page, have same set of rules on transmission. These standards define where and how the information from the document will be found. Translation software processes the information differently for sent and received messages and performs a complete audit of each step to ensure information is sent or received in EDI format. When the translator on the receiving computer reads a document, it knows where to find the buyer's company name, order number, purchase items and price, for example. This information is then sent to the receiver's order entry system without necessitating manual order entry.
EDI applies to documents such as purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices and commission sales reports, as well as other important or classified information. For an example, retailer can send the purchase orders to the suppliers in EDI exchange.
Some major sets of EDI standards:
- The UN-recommended UN/EDIFACT is the only international standard and is predominant outside of North America.
- The US standard ANSI ASC X12 (X12) is predominant in North America.
- GS1 EDI set of standards developed the GS1 predominant in global supply chain
- The TRADACOMS standard developed by the ANA (Article Number Association now known as GS1 UK) is predominant in the UK retail industry.
- The ODETTE standard used within the European automotive industry
- The VDA standard used within the European automotive industry mainly in Germany
- HL7, a semantic interoperability standard used for healthcare data.
- HIPAA, The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability ACT (HIPAA), requires millions of healthcare entities who electronically transmit data to use EDI in a standard HIPAA format.
- IATA Cargo-IMP, IATA Cargo-IMP stands for International Air Transport Association Cargo Interchange Message Procedures. It’s an EDI standard based on EDIFACT created to automate and standardize data exchange between airlines and other parties.
- NCPDP Script, SCRIPT is a standard developed and maintained by the National Council for Prescription Drug Programs (NCPDP). The standard defines documents for electronic transmission of medical prescriptions in the United States.
- Edig@s (EDIGAS) is a standard dealing with commerce, transport (via pipeline or container) and storage of gas.
- Many of these standards first appeared in the early to mid 1980s. The standards prescribe the formats, character sets, and data elements used in the exchange of business documents and form
Some of standard EDI data keywords would be like ORDER (Eancom order), ORDHDR (Tradacom order), INVOIC (Eancom invoice), INVFIL (Tradacom invoice), DESADV (Advance shipping notice), TUN (Tradanet user number – defines trading relationship between trading partners, SNRF ( sender reference number – an identification number for each data sent or received).
Explore more on EDI basics here.
Automating paper-based tasks improves data quality, and transactions are exchanged within seconds or minutes instead of days or weeks. EDI frees up staff time to work on more important tasks. Business-critical data is sent on time and tracked in real time by automating the transfer of data among applications across a supply chain. The system is expensive to implement and usually requires help from a consultant that specializes in the field.
EDI can be transmitted using any methodology agreed to by the sender and recipient, like FTP (File transfer Protocol), SFTP ( same as FTP but use secure shell protocol), HTTP, AS1 (based on SMTP and S/MIME) , AS2 , AS4 and many.
A sample EDI documents looks like,

Hope this article gives idea on the EDI technology, its data and its usage in business.
Please share your comments below !!
 prince
prince 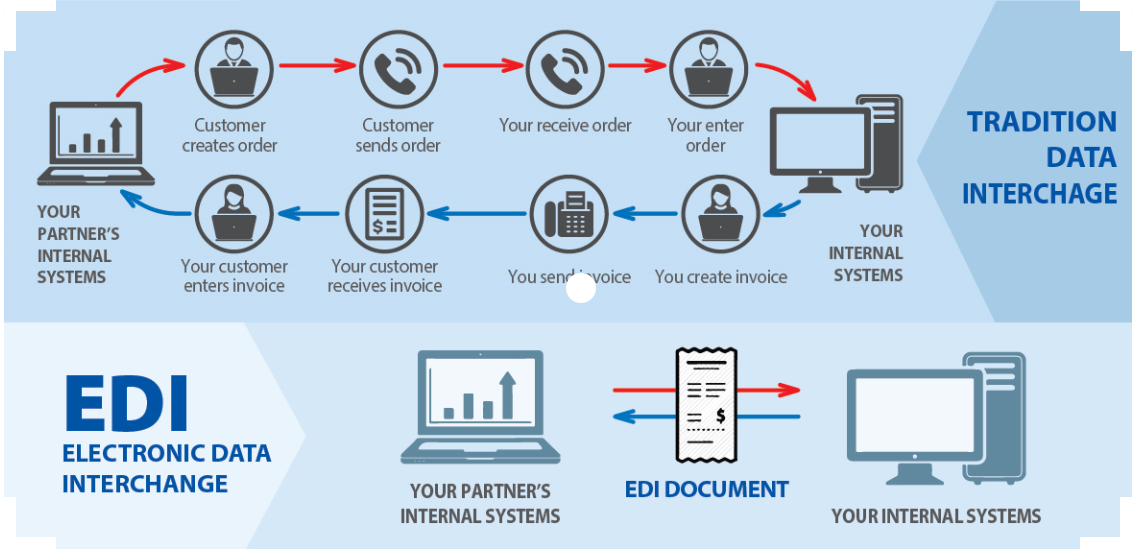
 Docker - DevOps
Docker - DevOps