What is Docker Machine?
Docker Machine is a tool that lets you install Docker Engine on virtual hosts, and manage the hosts with docker-machine commands. You can use Machine to create Docker hosts on your local Mac or Windows box, on your company network, in your data center, or on cloud providers like Azure, AWS, or DigitalOcean.
Using docker-machine commands, you can start, inspect, stop, and restart a managed host, upgrade the Docker client and daemon, and configure a Docker client to talk to your host.
Example:
docker-machine env default
- Run the above command to point to a host called default.
- Follow on the screen instructions to complete the env setup
- Run the docker commands like docker ps, docker run hello-world and so forth
Why should I use it?
Docker Machine enables you to provision multiple remote Docker hosts on various flavors of Linux. Additionally, Machine allows you to run Docker on older Mac or Windows systems, as described in the previous topic.
Docker Machine has these two broad use cases.
- I have an older desktop system and want to run Docker on Mac or Windows

If you work primarily on an older Mac or Windows laptop or desktop that doesn’t meet the requirements for the new Docker Desktop for Mac and Docker Desktop for Windows apps, then you need Docker Machine to run Docker Engine locally. Installing Docker Machine on a Mac or Windows box with the Docker Toolbox installer provisions a local virtual machine with Docker Engine, gives you the ability to connect it, and run docker commands.
- I want to provision Docker hosts on remote systems

Docker Engine runs natively on Linux systems. If you have a Linux box as your primary system, and want to run docker commands, all you need to do is download and install Docker Engine. However, if you want an efficient way to provision multiple Docker hosts on a network, in the cloud or even locally, you need Docker Machine.
Whether your primary system is Mac, Windows, or Linux, you can install Docker Machine on it and use docker-machine commands to provision and manage large numbers of Docker hosts. It automatically creates hosts, installs Docker Engine on them, then configures the docker clients. Each managed host (“machine”) is the combination of a Docker host and a configured client.
What’s the difference between Docker Engine and Docker Machine?
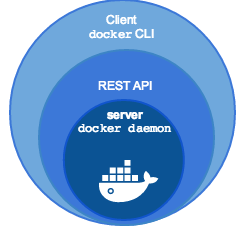
When people say “Docker” they typically mean Docker Engine, the client-server application made up of the Docker daemon, a REST API that specifies interfaces for interacting with the daemon, and a command line interface (CLI) client that talks to the daemon (through the REST API wrapper). Docker Engine accepts docker commands from the CLI, such as docker run <image>, docker ps to list running containers, docker image ls to list images, and so on.
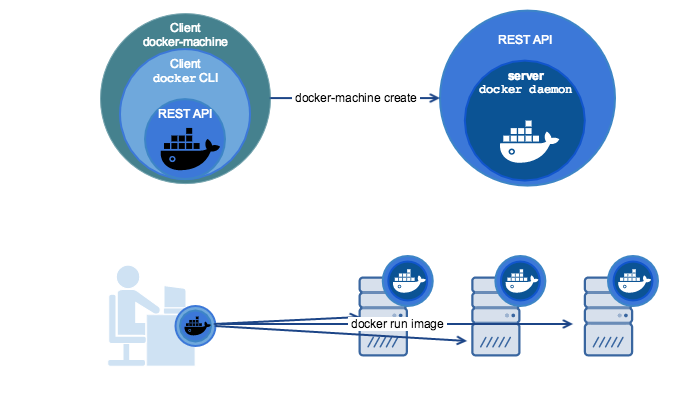
Docker Machine is a tool for provisioning and managing your Dockerized hosts (hosts with Docker Engine on them). Typically, you install Docker Machine on your local system.
Command line information:
- Docker Machine - docker-machine is the CLI
- Docker Engine - docker is the Command line interface
You can use Machine to install Docker Engine on one or more virtual systems. These virtual systems can be local (as when you use Machine to install and run Docker Engine in VirtualBox on Mac or Windows) or remote (as when you use Machine to provision Dockerized hosts on cloud providers). The Dockerized hosts themselves can be thought of, and are sometimes referred to as, managed “machines”.
 prince
prince 
 Undeletable & Unrenamable Folder
Undeletable & Unrenamable Folder